Medical Physics - Medical Applications
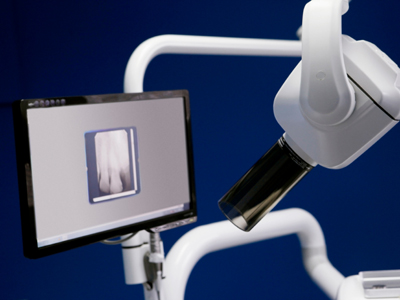
This GCSE Physics quiz looks at medical applications. A knowledge and understanding of physics is widely used in medical applications to provide better treatment and prevention of illness and ailments. Probably the first to spring to mind is the use of X-rays for examining broken bones, but there are many more such as Computerised Tomography (CT) scanning machines and endoscopes. Radioisotopes can be injected or swallowed and their radioactivity can be measured from outside of the body. This enables doctors to follow how the body is working. Medical radioisotopes have short half-lives and do not emit alpha particles. Inside the human body, alpha particles are the most damaging form of radiation.
For the GCSE, you are required to know about X-rays and ultrasound for scanning, and about using light for image formation with lenses and endoscopes.
Ready for more?
not all...
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.







