Atomic Structure 1
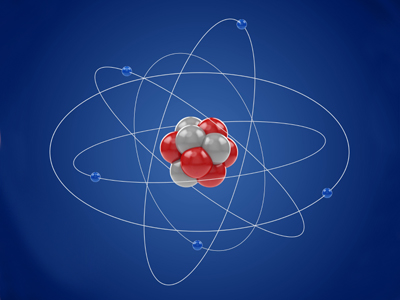
The study of atomic structure forms a major part of GCSE Chemistry. This includes many aspects such as the sub-atomic particles (protons, neutrons and electrons) and their arrangement within the atoms of different elements; atomic mass; atomic number; positive and negative charge; the nucleus; energy levels or electron shells - to name but a few!. Therefore, we have three quizzes devoted to this particular topic, of which this is the first.
The word atom comes from the ancient Greek word atomos meaning unsplittable or uncuttable. A philospher called Democrites carried out a thought experiment. He imagined taking a piece of rock and hitting it with a hammer. He knew the rock would break so he wondered what might happen if you took one of the broken pieces and hit that and so on. He arrived at the conclusion that you would eventually be left with a piece that was so small it could not be broken any more.
The atomic number is also called the proton number because it tells you the number of protons in the nucleus. For the GCSE, you need to know that elements are neutral atoms. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons orbiting the nucleus is the same as the number of protons within the nucleus. If you are not sure why, ask your science teacher to explain
The mass number shown in the Periodic Table is an average of the mass of the isotopes
Ready for more?
not all...
quizzers. Try to win a coveted spot on our Hall of Fame Page.







